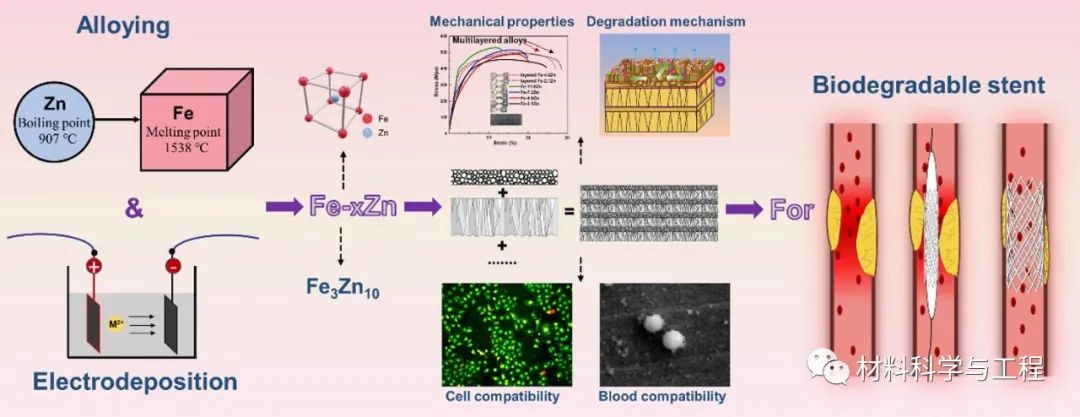
Mg、Fe、Zn三類金屬及其合金是應用最多、研究最廣的生物可降解金屬支架材料。其中金屬Fe具有良好的生物相容性和機械性能,是發展最早,也是最有潛力替代永久性支架的材料之一,但它相對較慢的降解速率一直是制約其發展的關鍵問題。
為解決這個問題,大連理工大學材料學院王偉強團隊提出將活性更高的Zn與Fe合金化,制備以Fe為基體的Fe-Zn合金,有望滿足降解速率要求,同時保留鐵的固有機械性能。而Zn與Fe熔沸點差距大,給材料制備也增加了難度。為獲得質量較好的Fe-Zn合金,用電沉積來替代傳統的冶金手段不僅可以獲得熔沸點差距較大的二元合金,同時這種原子級的互競共沉積也可以得到亞穩態的Fe-Zn合金,進一步提高材料的腐蝕速率。在這份工作中還對合金進行了層狀結構設計,通過調控電參數,制備了納米晶和超細柱狀晶組織交替生長的層狀結構。評估了合金的成分、微觀結構、機械性能、體外降解性能和生物相容性。
研究結果顯示,所有合金的基體均為亞穩態的有序固溶體相,其中只有Zn含量提高到11.6%時才有細小的第二相析出(室溫下Zn在Fe中的溶解度小于2%)。層狀Fe-Zn合金的屈服強度超過350MPa,延伸率超過20%,并且通過浸泡測試所得的腐蝕速率高達0.367mm/y。不僅如此,層狀設計還解決了Fe基材料的局部腐蝕問題。在隨后的血液相容性和細胞相容性測試中,低Zn含量的單層和多層Fe-Zn合金均表現出良好的生物相容性。該研究以“The enhancement of mechanical properties and uniform degradation of electrodeposited Fe-Zn alloys by multilayered design for biodegradable stent applications”為題發表在生物材料領域的權威期刊《Acta Biomaterialia》上。
文章連接:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2023.02.029
文章整體思路
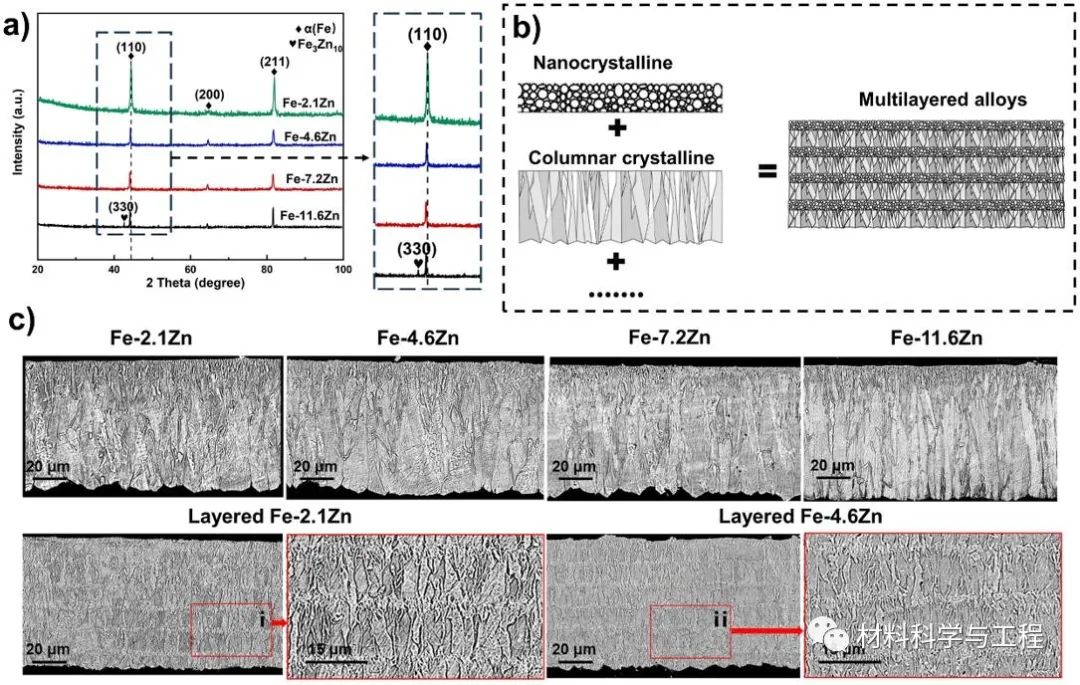
Fig. 1. (a) XRD patterns of the electrodeposited Fe-Zn alloys and the magnification of diffraction peak of (110). (b) Schematic diagram of the microstructure of multilayered alloy. (c) The microstructure of Fe-Zn alloys with monolayered structure and multilayered structure and the enlarged view of areas ⅰ and ⅱ of multilayered alloys.
Fig. 2. The TEM analysis of Fe-Zn alloys.
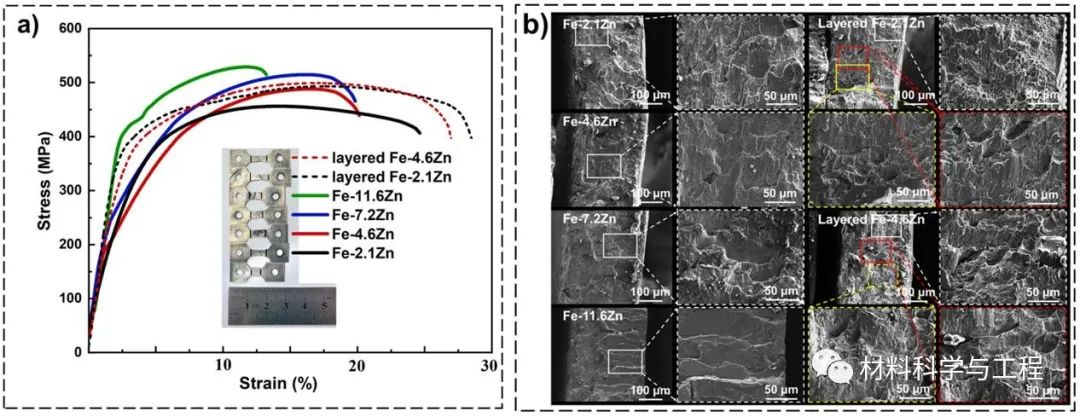
Fig. 3. Tensile properties of Fe-Zn alloys. (a)The tensile curves. (b)Fracture morphologies observed by SEM.
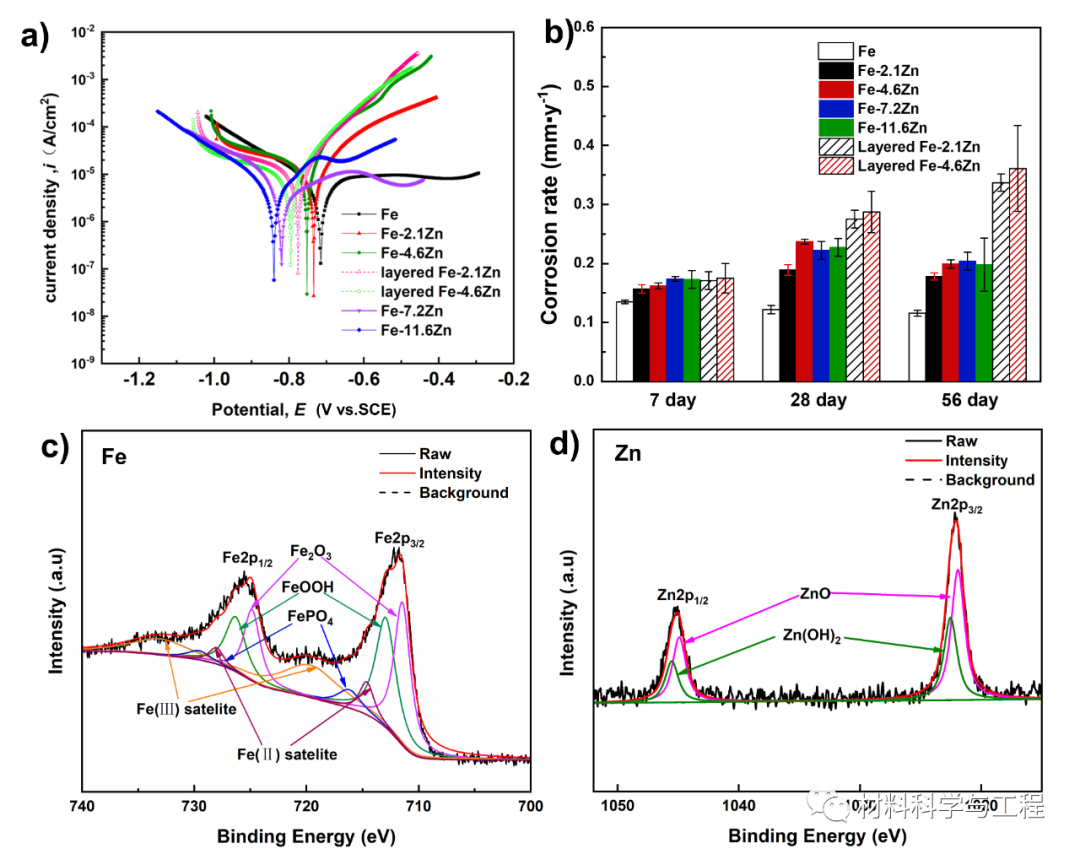
Fig. 4. Corrosion assessment of the Fe-Zn alloys. (a) Potentiodynamic polarization curves. (b) The corrosion rate measured by the weight-loss method after immersion test. (c and d) XPS spectra of Fe-11.6Zn alloy after immersion.
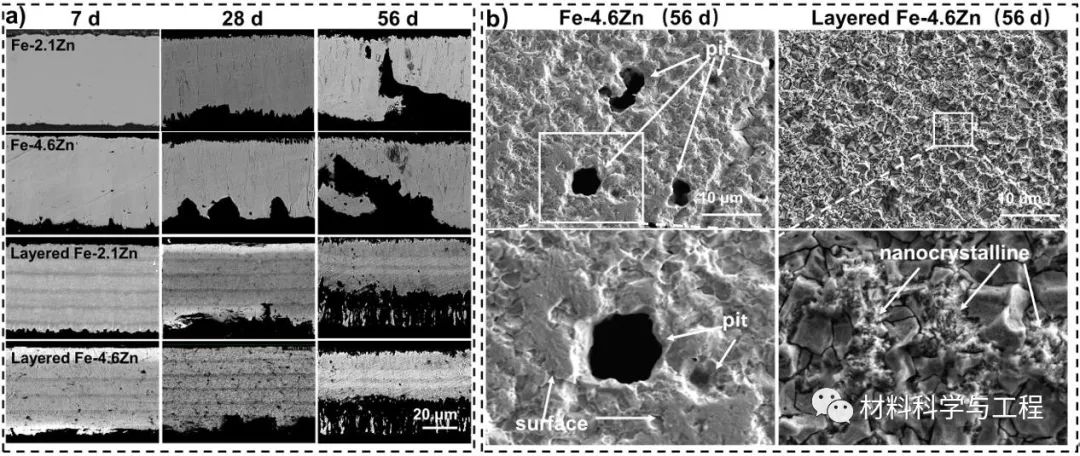
Fig. 5. The corrosion morphologies of Fe-Zn alloys. (a) Cross-section morphologies of Fe-Zn alloys after immersion test for 7, 28, 56 d. (b) Surface morphologies of Fe-4.6Zn and layered Fe-4.6Zn after immersion test for 56 d.
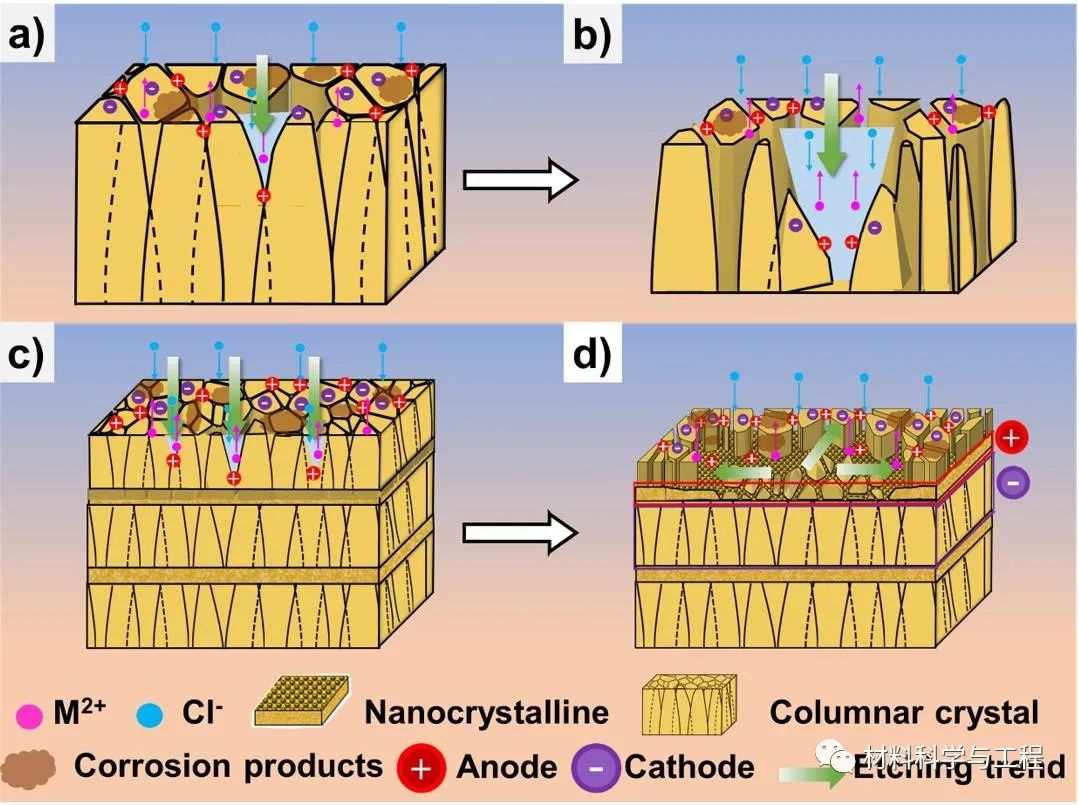
Fig. 6. Schematic diagram of corrosion mechanism of monolayered (a, b) and multilayered Fe-Zn alloys (c, d) at the initial (a, c) and later (b, d) stages of immersion test.
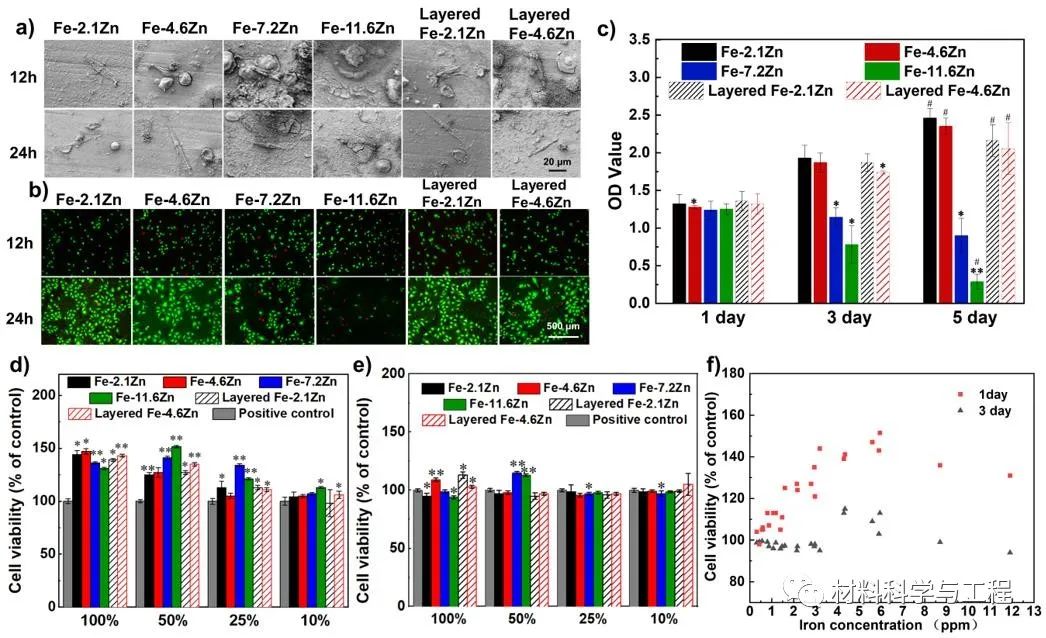
Fig. 7. Cytotoxicity assessment of HUVECs on the surfaces and in the extracts of the Fe-Zn alloys.
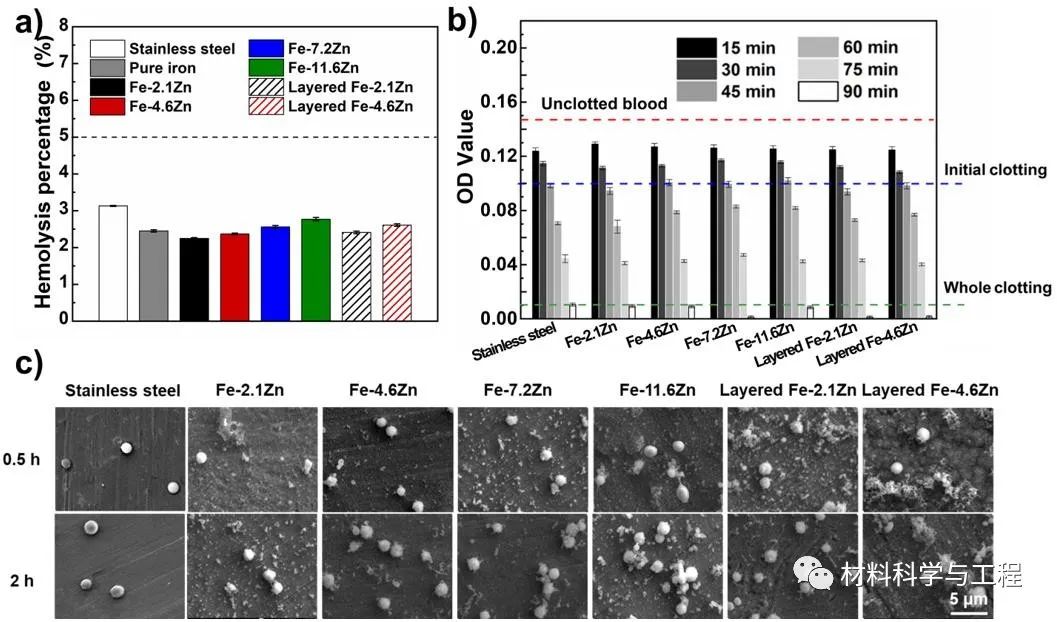
Fig. 8. Blood compatibility tests on the Fe-Zn alloys (316L stainless steel as control). (a) Hemolysis rates of stainless steel and Fe-Zn alloys. (b) The whole blood clotting on different surfaces for up to 90 min. (c) The adhesion morphology of platelets on Fe-Zn alloys.
綜合上述分析,電沉積所制備的層狀Fe-Zn合金很有希望能滿足生物可降解支架的應用標準,開創鐵基材料在冠心病介入治療領域的新篇章。
免責聲明:本網站所轉載的文字、圖片與視頻資料版權歸原創作者所有,如果涉及侵權,請第一時間聯系本網刪除。

官方微信
《腐蝕與防護網電子期刊》征訂啟事
- 投稿聯系:編輯部
- 電話:010-62316606-806
- 郵箱:fsfhzy666@163.com
- 腐蝕與防護網官方QQ群:140808414